
It simply means that your image will retain its quality regardless of how you enlarge it. Nonetheless, worry not as this does not mean you'll be dealing with calculus during editing. That is why you'll sometimes hear someone refer to the lines, shapes, and curves of a vector-based graphic as vertices and paths. The resolution of vector images is often dictated by mathematical equations. Vector-based data is often made up of various lines, shapes, and curves. This explains why they are a preferred option when it comes to web applications. While on the one hand, it's a downside, on the other hand, the pixel-based structure of a rasterized image is also an advantage as it can be scaled down to fit applications that require small-detailed images. Thus, if space is an issue for you, it would be wise to downsize. You will, nonetheless, need a bigger disk as more pixels in an image mean that it'll use more disk space. Therefore, to ensure your raster-based images are of the best quality possible, use more pixels. Thus, the more pixels present per inch(PPI), the better the resolution and vice versa.

The resolution of a raster image is however dictated by the number of pixels in every inch. When you zoom in or enlarge, you're practically forcing your device to create non-existent pixels, hence the pixelation.

While raster graphics are popular, it's vital to note that due to their pixel-based structure, they tend to be grainy or blurry when resized or enlarged. Some of the most common raster formats include: In most cases, these pixels are square-shaped, regularly spaced, and each one carries a specific shade, which contributes to the vivid and detailed appearance of the image.
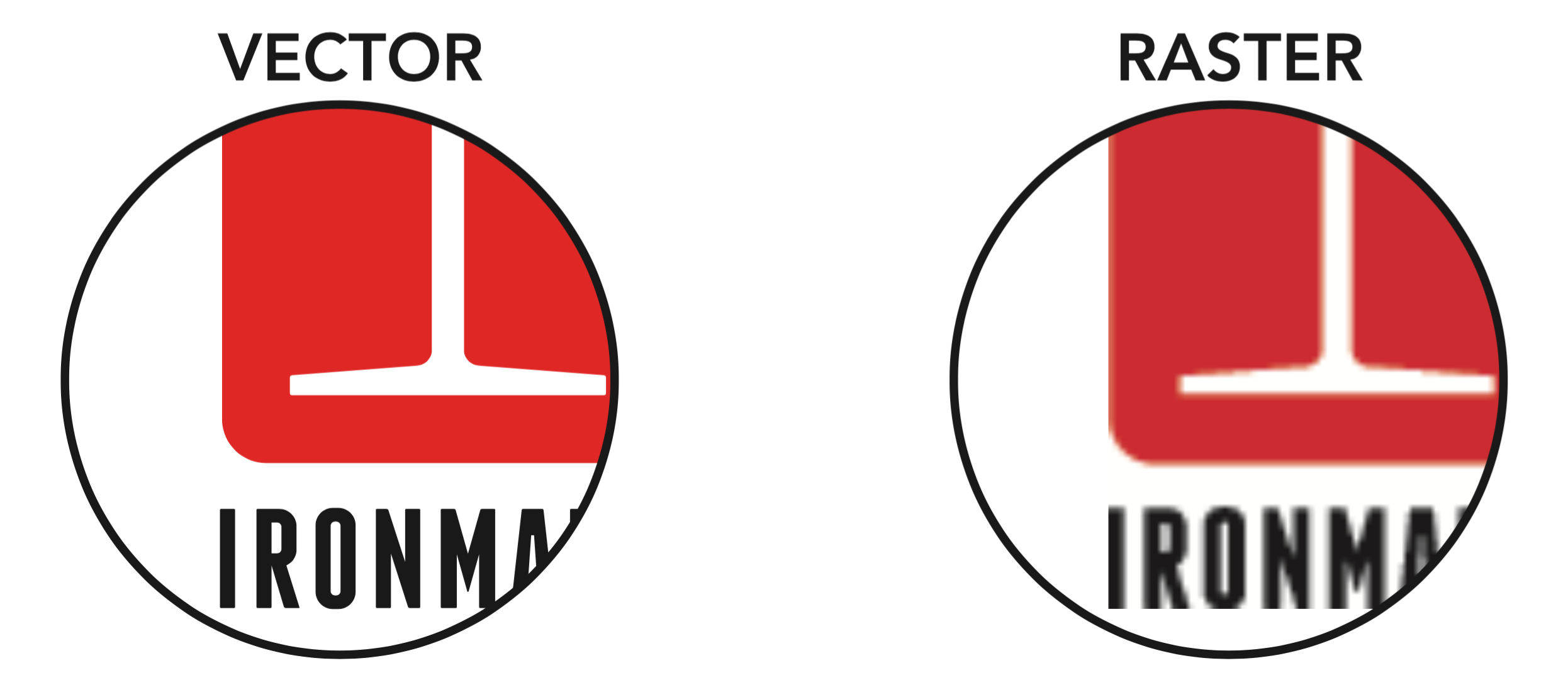
Also known as a bitmap, a raster image is a graphic made up of thousands or even millions of colored dots known as pixels. If you use the internet every day, then you encounter raster graphics daily.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
